Physico- Chemical Structure of Polymer,
Polymers are difficult to classify because there are so many interacting relationship among the large number of polymeric materials now in existence.
Four most
methods of classifications are
1. Physico chemical structure
2. Mode reparation
3. Physical properties
4. Technical applications
A. Physico Chemical structure
Functionality: - The ultimate
result of coupling monomers to produce polymers is wholly dependent on the
functionality of monomer. Molecule is called Mono-, bi-,tri-, or polyfunctional
depending on the number of reactive bonds or groups available for coupling at
beginning or during course of polymeric reaction.
1. Unifunctional (U-), Example: CH3.COOH where carboxyl (COOH)
group is the oly chemically reactive group.
2. Bifunctional (-B-) ex. CH2=CH2, where the double
bond splits to form coupling with another molecule containing double bond, Not necessarily
ethylene .
Polyethylene
= –(CH2-CH2)-
3. Trifunctional : - (-T-) Example : Trimethylol phenol made from phenol
and formaldehyde
The three OH group on
the methylol linkage are reactive.
B. Physical Structure and
functionality,
a. Linear polymers : – Formed from bifunctional group
… -B-B-B-B-B-B-B-B-…
This type of polymer is normally
thermoolastic (Creep flow at temperature >150 0 C)
b. Cross linked polymer : - formed from bi and tri functional
groups e.g.a
![]()
![]() ….B-B-B-B-B-T-B-T-B-….
….B-B-B-B-B-T-B-T-B-….
B-B-T-B-T-B-B-B-….
Cross linkage in three dimensions
gives elastomeric properties if there are only a few such bond across linear polymer
chains.
If bonding is more extensive,
solidified thermoset polymers result with high resistance to heat and
mechanical deformation
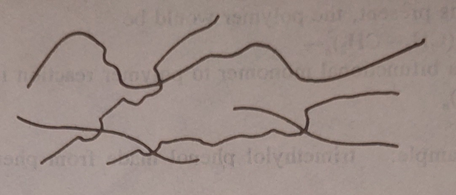
c. Branched chain polymer: an intermediate case where braches
grow from the parent chain with our cross linking.
![]() B-B-B-
B-B-B-
![]() ….B-B-T
….B-B-T
B-B-B-
Branching is caused by small amounts
of -T- often as impurities, Present in a bifunctional monomer formulation. The effect
is to lower solubility. Increase softening point and reduce thermoplastic
forming properties,





Comments
Post a Comment